Geometry Ace: Math Tutor
Geometry Ace is a fusion between a graphics based calculator and a geometry textbook. Detailed step-by-step solutions update as you create new math problems by changing the graphics. Learn vocabulary with unlimited examples. Points, Lines, Segments, Rays, Angles, Triangles, Quadrilaterals, Polygons, and Circles. Transformations and Constructions. Full functionality with no ads or in-app purchases. Great classroom or home resource for elementary, middle, and high school students and teachers.
*** Easy Start-up ***
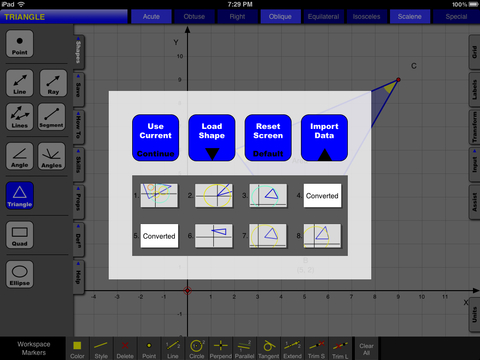
• Simply choose shape to study.
• Shape will already be on the screen and all you have to do is start manipulating it.
• Learn vocabulary, choose from list of tutorials, perform transformations, or create a construction.
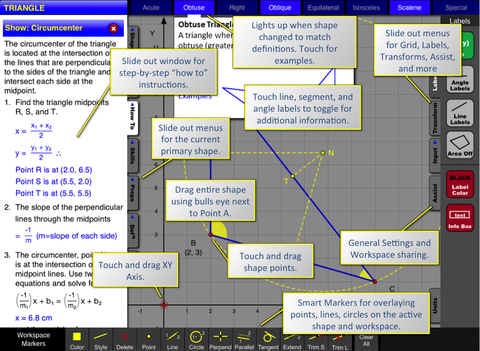
*** Detailed problem solutions update as you change the graphics. ***
• You are not limited to a set of pre-written or randomly generated problems.
• Tutorial examples: finding the length of a line segment, finding the area of any type of quadrilateral, calculating the length of an arc, and many more.
• Geometry Ace does not simply calculate lengths and areas for you. It shows you step-by-step how to do it!
*** Includes introductory material and makes connections with algebra. ***
• Introductory material appropriate for upper elementary students is included.
• Helps with differentiation. Middle and high school students who need a refresher can review introductory topics.
• Algebra topics needed for coordinate geometry are included.
• Introductory topics include coordinates of a point, slope, and the equation of a line.
• Answers to problems are given in fraction form when possible.
• Solutions address common student misconceptions and give attention to detail.
*** Interactive definitions ***
• Relevant definitions highlight interactively as you drag points and lines to change the shape on the screen to meet various attributes.
• Example: A triangle can be obtuse, oblique, and scalene.
• Example: A polygon can be concave and irregular.
• Definitions are inclusive. Example: A quadrilateral that is a rectangle is also a parallelogram and a trapezoid.
*** Transformations: Rotations, Reflections, and Translations ***
• Easily change degrees of rotation, center of rotation, line of reflection, and translation vector.
• Point mapping is shown!
• Perform successive transformations on the same object.
*** Constructions ***
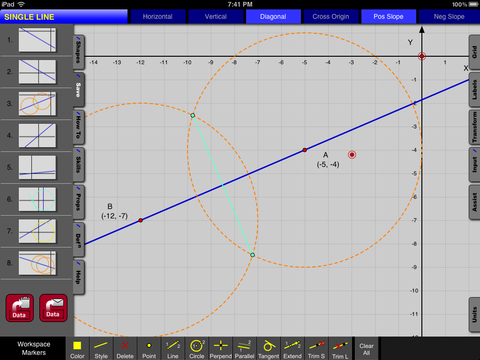
• Includes points, lines, segments, circles, perpendicular lines, parallel lines, tangents, and angle bisectors.
• Easily make attachments to points, lines, circles, intersections, and midpoints.
*** Monitor Students ***
• Teachers can view student’s iPad screens who are on the same local wifi network and running this app.
TOPICS AVAILABLE IN GEOMETRY ACE
POINT:
Coordinates
Quadrants
Distance between points
LINE/RAY/SEMGENT:
Slope
Vertical, Horizontal
Y-intercept
Equation of line/ray/segment
Distance between point and line
Construct or write equation of parallel or perpendicular line
Segment midpoint and length
Construct or write equation of perpendicular bisector
Intersection point of 2 lines
Transversals
Alternate interior angles
Alternate exterior angles
Corresponding angles
Same side interior angles
Vertical angles
ANGLE:
Vertex, Legs, Interior, Measure
Acute, Right, Obtuse, Straight, Reflex
Convert between degrees/radians
Construct or write equation for angle bisector
Congruent, Adjacent, Complimentary, Supplementary, Linear Pair, Vertical
TRIANGLE:
Acute, Obtuse, Right, Oblique, Equilateral, Isosceles, Scalene
Perimeter
Area – basic elementary
Area – coordinate plane - algebra
Area – box method
Centroid, Circumcenter, Incenter
QUADRILATERAL:
Square, Rectangle, Rhombus, Parallelogram, Trapezoid, Kite
Perimeter
Area
POLYGON:
Triangle, Quadrilateral, Pentagon, Hexagon, Heptagon, Octagon, Nonagon, Decagon
Convex, Concave
Regular, Irregular
Sum of interior angles
CIRCLE:
Radius, Diameter, Tangent, Secant, Chord
Circumference
Area
Measure and length of an arc
Area of a sector